|
|
이전 질문 게시판은 새 글 쓰기를 막았습니다. [질문 게시판]을 이용바랍니다.
| Date |
2008/03/01 23:04:31 |
| Name |
wannabein |
| File #1 |
noname01.jpg (3.6 KB), Download : 3 |
| Subject |
공대생중에서 SFA 혹시 아시는분 계신가요 |
PGR에 유능하신 공대생분들이 많으신거 같아서 여기에 여쭤봅니다
surface force apparatus라고 해서 물리적 측정에 있어 기본적인 기기 같은데
이쪽이 전공분야가 아니라서 원리를 정확하게 이해를 못하고 있습니다
표면력을 측정하는 기기 같은데 표면력이라는게 대체 뭐고
표면력을 이용하여서 분자의 표면 상태를 확인하는건가요?
밑에는 science에 나온 논문에서 SFA에 대해 대표적이라는 걸 옮기는데 봐도 정확하게 이해가 안되네요
그리고 논문에서 M에 해당하는게 두 원통을 고정하는 고정대의 이동을 이야기 하는거 같은데
왜 M=D인지 (계산을 쉽게 하기 위한 기본 설정인지)
마지막으로 왜 표면력을 F라 표기하지 않고 F(D)로 표기하고 거리를 D(M)이라 했는지 알고계시는분 없나요?
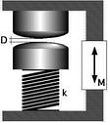
The Surface Forces Apparatus (SFA) is an instrument that can measure forces occuring between two curved surfaces. The two surfaces are cylindrically curved and oriented such that the cylinder axies are crossed at an angle of 90°. The shortest distance, D, between the two curved surfaces can be varied by moving the approach actuator by the amount, M. One of the two surfaces is mounted on a compliant spring with spring constant, k. When the surfaces are separated sufficiently, a motion of the actuator will result in an equal change in surface distance; i.e. M=D.
The situation is different when a surface force, F(D), deflects the spring at closer distances and D and M are thus no longer equal.During an experiment one optically measures D(M) to be able to calculate the external force, F(D)=k*(D-M). A negative force means attraction and a positive force means repulsion. When the surfaces are in contact, they deform elastically to form a circular contact with a diameter of several 10µm. In such contact, D may vary only little, while the actuator continues to move. Then, the external force (or load), F is increased roughly proportional to k*M.
For the measurement, it is of utmost importance that M can be controlled very accurately and reproducibly. A well-designed mechanical approach mechanism is necessary to meet these requirements.
Common surfaces are 2-5µm thick sheets of mica, which are manually cleaved and glued onto transparent cylinder lenses after evaporation of a typically 55 nm-thick silver layer on the reverse side. The two silver layers are mirrors comprising the white light interferometer. Using Multiple Beam Interferometry (MBI), one can determine the distance between the surfaces. To this end, it is necessary to measure an optical zero when the mica surfaces are in direct contact. The measurement of the optical zero is essentially a determination of the mica substrate thickness.
A number of attachments have been developed for the SFA, which allow one to apply and measure oscillatory or linear motions in-plane and out-of-plane. The best known example is a lateral-force attachment, which can be used to study friction in the SFA.
|
통합규정 1.3 이용안내 인용
"Pgr은 '명문화된 삭제규정'이 반드시 필요하지 않은 분을 환영합니다.
법 없이도 사는 사람, 남에게 상처를 주지 않으면서 같이 이야기 나눌 수 있는 분이면 좋겠습니다."
|